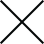
Dermatologists may be the first to recognize the signs of BPDCN because ~90% of patients present with skin lesions1-5
Deep purple nodular lesions3
- Most common cutaneous manifestation in BPDCN patients3
- May be single or multiple and are localized to various areas, particularly the trunk, limbs, and head3,6
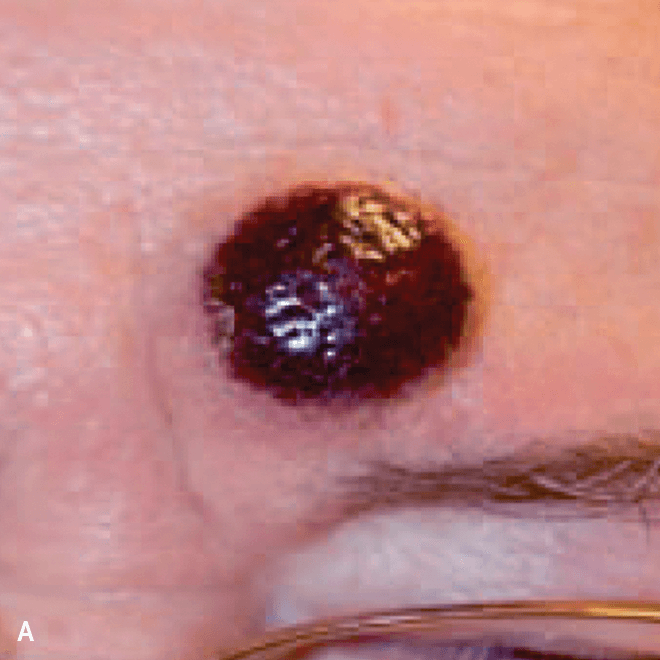
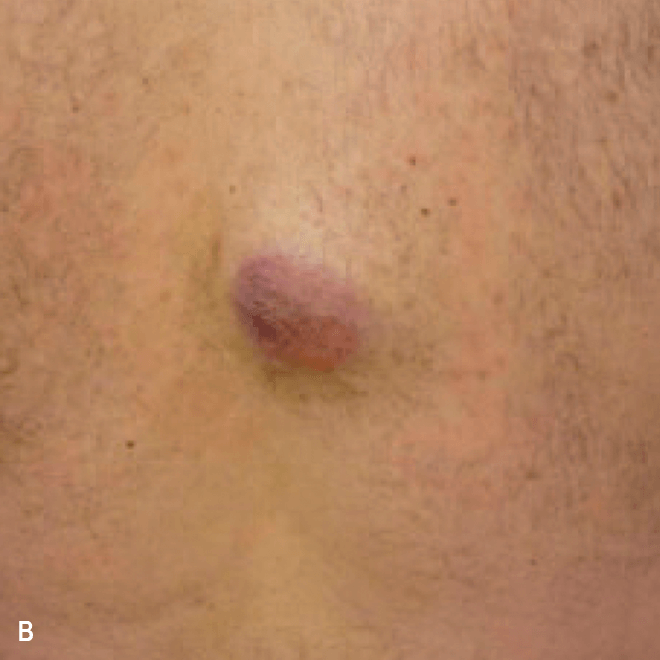
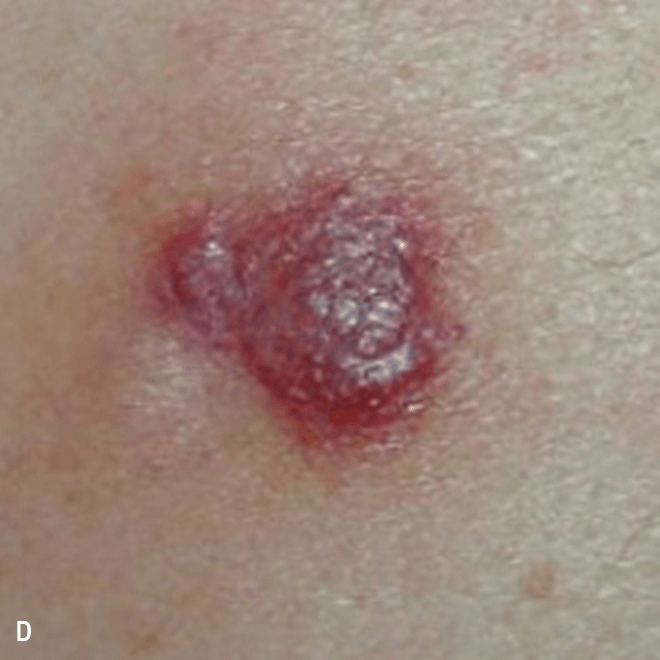
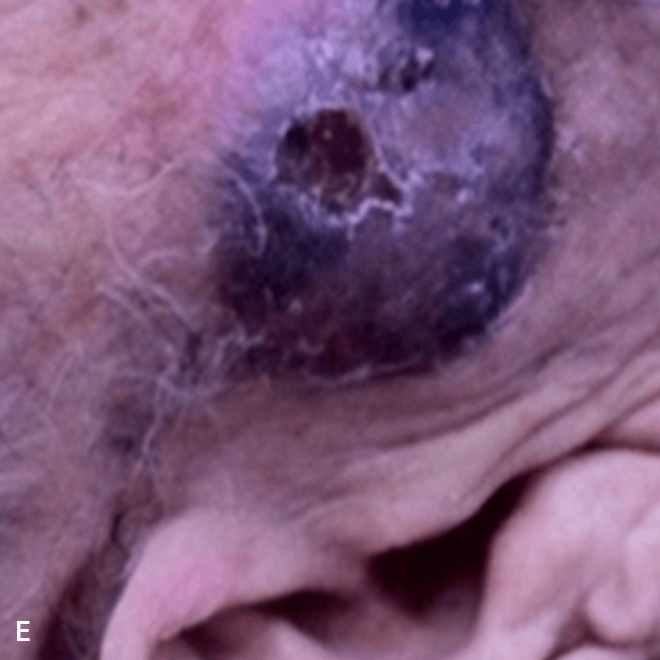





A. and B. Julia F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: clinical features in 90 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):579-586, published by John Wiley and Sons. © 2013 The Authors BJD © 2013 British Association of Dermatologists. C. Courtesy of Shapiro R, et al. J Cell Sci Ther. S8:008. doi:10.4172/2157-7013.S8-008 D. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: Modern Pathology, Neoplasms derived from plasmacytoid dendritic cells, Facchetti F, © 2016. E. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.
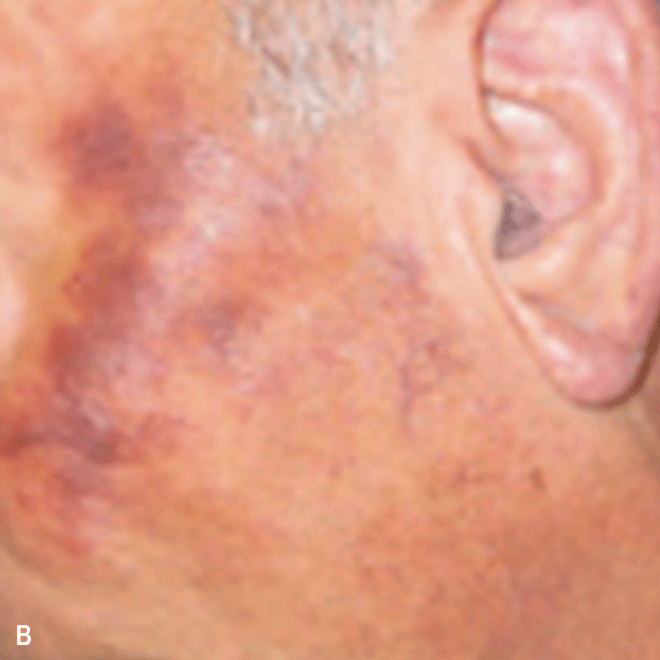
Diffuse bruise-like or hyperpigmented red-brown macules2,7
- May be small and/or diffuse; one or several bruise-like patches confined to various body areas3
- Some patients present with disseminated and mixed lesions6
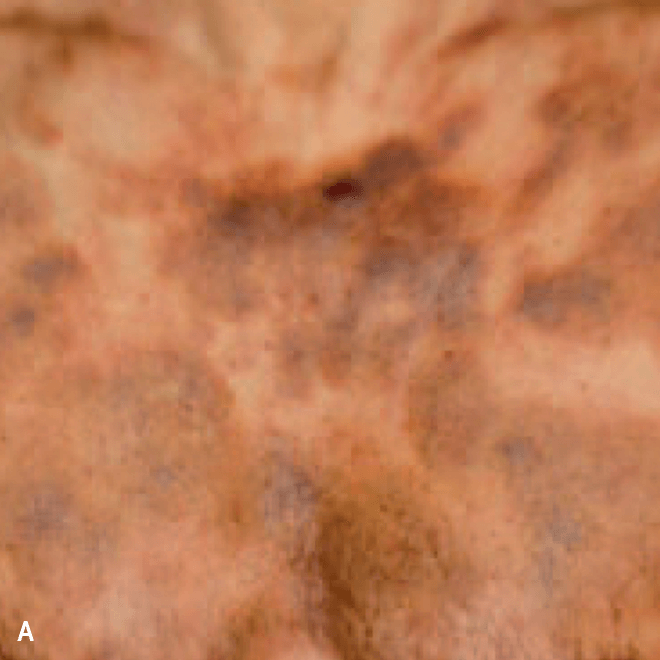
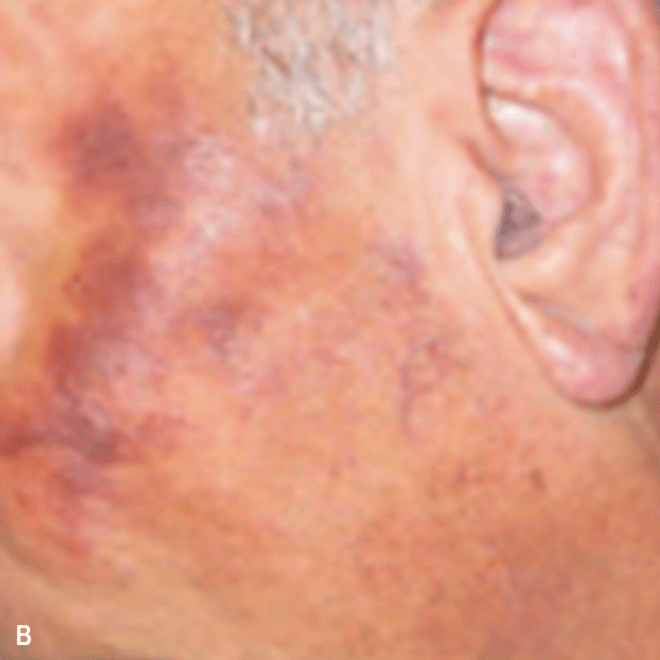
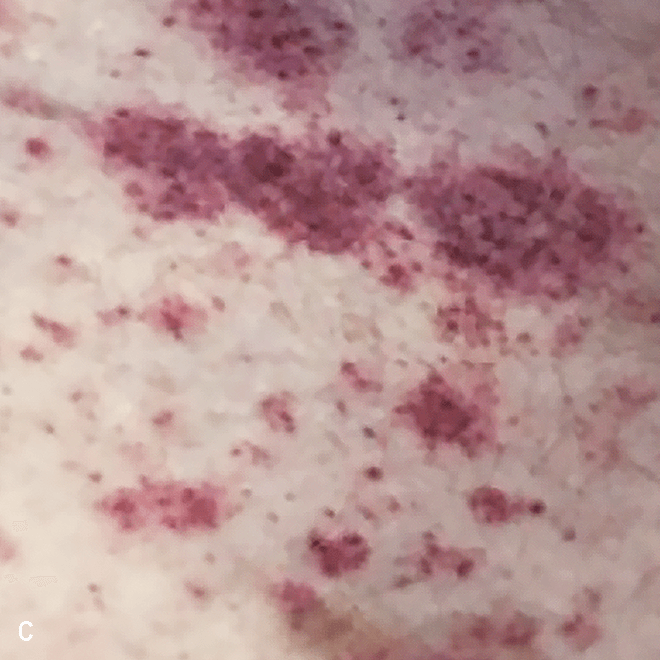
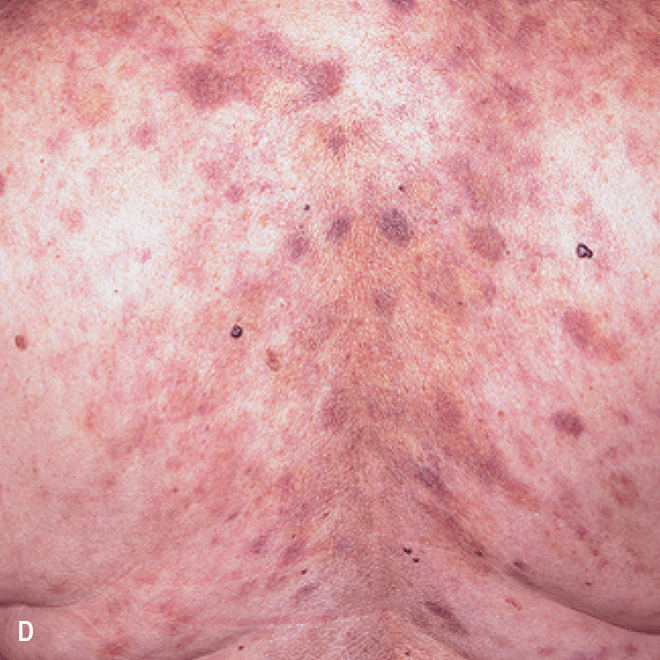
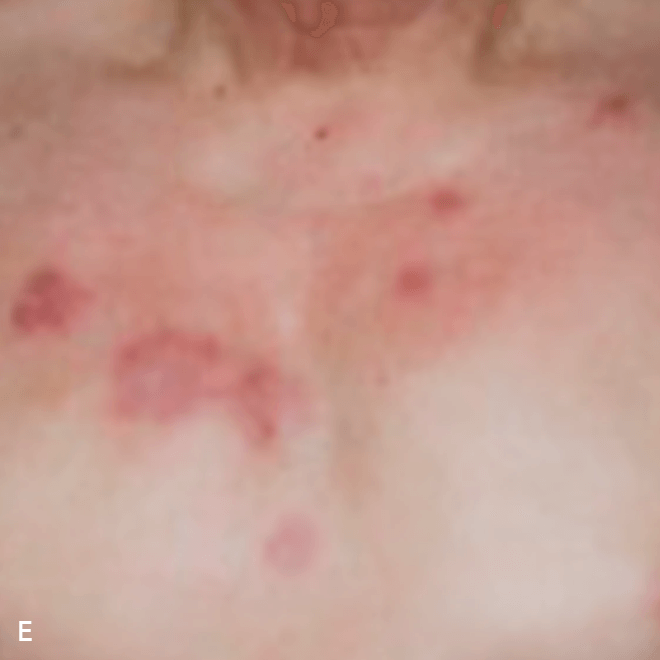
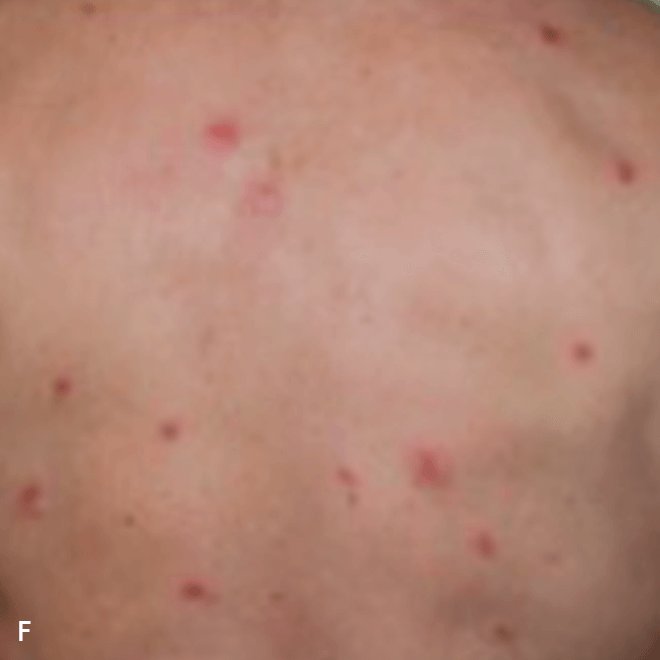





A. and B. Julia F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: clinical features in 90 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):579-586, published by John Wiley and Sons. © 2013 The Authors BJD © 2013 British Association of Dermatologists. C. Republished with permission from American Society of Hematology. D. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society. E. and F. Reprinted with permission of Blood.
Diffuse bruise-like macules can be mistaken for benign bruising2,3
Important to know
- Skin lesions:
- Vary in size, shape, distribution, and color, and are often nonpruritic4,7
- May be localized or disseminated5
- May become scaly over time4
- Hyperpigmented macules can be mistaken for neoplastic and non-neoplastic etiologies2
- In a retrospective analysis, the mean time between the onset of lesions and the final diagnosis of BPDCN was
6.2 months3
Skin biopsies are often key to diagnosis and should include deep dermis, as BPDCN typically spares the epidermis5,8
BPDCN, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm.
- References:
- Pagano L, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: diagnostic criteria and therapeutical approaches. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(2):188-202.
- Sullivan JM, Rizzieri DA. Treatment of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016;2016(1):16-23.
- Julia F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: clinical features in 90 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):579-586.
- Laribi K, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: from origin of the cell to targeted therapies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(8):1357-1367.
- Hirner JP, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: the dermatologist’s perspective. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020;34(3):501-509.
- Reichard KK. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: how do you distinguish it from acute myeloid leukemia? Surg Pathol Clin. 2013;6(4):743-765.
- Riaz W, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: update on molecular biology, diagnosis, and therapy. Cancer Control. 2014;21(4):279-289.
- Facchetti F, et al. Neoplasms derived from plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mod Pathol. 2016;29(2):98-111.